Fields overview
Supported field types
Front Matter its metadata section supports the following fields:
stringnumberdatetimebooleanimagefilechoicelistdraft: specifies the kind of draft field you want to use:booleanorchoice. This field, can be configured with the frontmatter.content.draftfield setting.tags: mapped to the tags defined in your settings.categories: mapped to the categories defined in your settings.taxonomy: if you want to define your own custom taxonomy fields.fields: allows you to define another object and its fields.block: allows you to define a group of fields which can be used to create an list of data.dataFile: allows you to use a data file reference to create a choice fieldslug: allows you to manage the slug of the current page
Standard field properties
All fields share the following field properties:
title (string): The title to show in the metadata section (optional);name (string): The name of your field, will be used to set in the front matter of your Markdown file;type (field type - string): One of the above supported types.default: Defines the default value for the field when creating the content type. You can also use placeholders like{{title}},{{slug}}or{{now}}. Check for more information under placeholders.hidden (boolean - optional): Specifies if you want to hide the field from the metadata section, but still have it available in Front Matter.
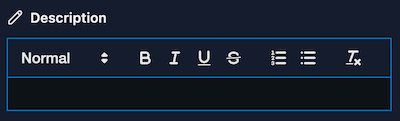
String
The string field type is used to store a single-line or multiline of text. For instance, you can use if for the title, description, or any other text field.
Properties
single (boolean): When you picked thestringfield type, you can specify if it is a single line. By default it will render as a multiline field (optional).wysiwyg (boolean): When you set this value totrue, the field will be rendered as a WYSIWYG editor. The output of the WYSIWYG editor will be HTML.
Usage
Outcome
Number
The number field allows you to insert integer values, like for instance setting the weight of your content.
Usage
Outcome
Datetime
The datetime field allows you to add date fields. You can use it for publish, modified, and any other types of dates for you content.
Properties
isPublishDate: Specifies if the field is a publish date. When set totrue, the field will be used to set the publish date for the content (this will be reflected on the content dashboard).isModifiedDate: Specifies if the field is a modified date. When using thefrontMatter.content.autoUpdateDatesetting to automatically update the modified date of the article, this field will be used.
The format of your date can be defined in the
frontMatter.taxonomy.dateFormatsetting. Check date-fns formating for more information.
Usage
Outcome
Boolean
The boolean field can be used to set a value of true or false into your markdown. It will be rendered as a toggle.
Usage
Outcome
Choice
The choice field allows you to define a set of options.
Properties
choices (string[] | { id: string; title: string; }): When you picked thechoicefield type, you need to return an array of choices.multiple (boolean): Define if you want to allow multiple choice selection. By default this isfalse.
Usage
Example of using an array of string values:
Example of using an array of { id: string; title: string; } objects:
Outcome
Outcome when using string values:
Outcome when using id/title objects:
List
The list field allows you to add multiple text values.
Usage
Example of using the list field:
Outcome
The previous example will give you the following outcome:
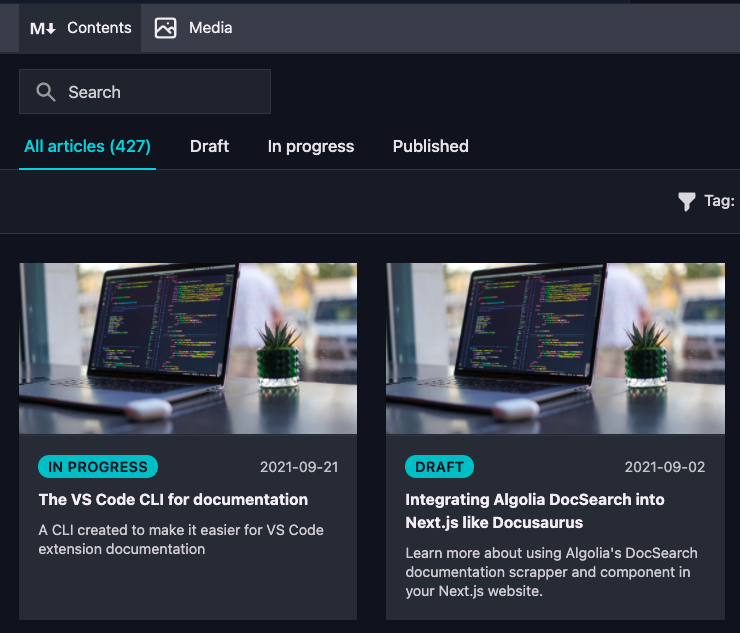
Draft
The draft field defines the state of your content. This is used for the content dashboard as well. By default, the draft field is a boolean. If you want to use your own status values, you can configure it via the frontmatter.content.draftfield setting.
When using a custom draft status, the content dashboard will make use of it as well:
Important: If you use Jekyll, you do not have to use the draft field, as Front Matter supports the
_drafts,_postsfolders and collections from Jekyll. If you use Jekyll, make sure to set thefrontMatter.framework.idsetting tojekyll.
Example 1
Usage
Outcome
Default draft field outcome:
Example 2
Usage
In case you want to use a published field, instead of a draft field. You can invert the logic by setting the invert property to true:
The field is configured as follows:
Outcome
Default draft field outcome:
Example 3
Usage
If you want to use your own status values, you can define it by specifying these in the frontMatter.content.draftField setting:
The field is configured as follows:
Outcome
When using your own status values:
Image
The image field can be used to reference single or multiple images to your content.
Properties
isPreviewImage (boolean): Allows you to specify a custom preview image for your article. When you set this totruefor an image field in your content type, it will be adopted in the dashboard.multiple (boolean): Define if you want to allow to select multiple images. By default this isfalse.
Important: You can only set this on one image field per content type.
Usage
Outcome
File
The file field can be used to reference single or multiple files to your content.
Properties
multiple (boolean): Define if you want to allow to select multiple files. By default this isfalse.fileExtensions (string array): Define the file extensions that are allowed to be selected. By default this is an empty array[].
Usage
Outcome
Tags
The tags field allows you to create or use tags from your frontMatter.taxonomy.tags setting (by default, none existing). When adding a tag which does not yet exist, you will have the option to create it.
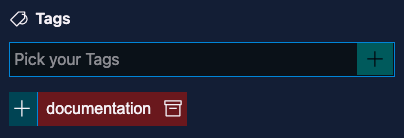
When the tag is created, you will be able to re-use it for other content.
Info: You can add multiple tags at once by entering them as comma-separated values and pressing the ENTER key.
Properties
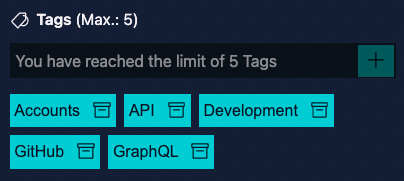
taxonomyLimit: Defines the maximum number of items that can be selected. By default set to0which allows unlimited items to be selected.
Info: When a limit is defined, this will get reflected in the UI as well:
Usage
Outcome
Categories
The categories field is similar to the tags field. The difference is that it uses the frontMatter.taxonomy.categories setting (by default, none existing).
Properties
taxonomyLimit: Defines the maximum number of items that can be selected. By default set to0which allows unlimited items to be selected.
Usage
Outcome
Taxonomy
The taxonomy is similar to the tags and categories field, but allows you to define your own taxonomy values and structure.
Properties
taxonomyLimit: Defines the maximum number of items that can be selected. By default set to0which allows unlimited items to be selected.taxonomyId: Set the id of your custom taxonomy definition defined in thefrontMatter.taxonomy.customTaxonomysetting.
Custom taxonomy
The frontMatter.taxonomy.customTaxonomy setting allows you to provide a list of custom taxonomy data. Each of the taxonomy data contains a id and an array of options.
Here is an example of the custom taxonomy setting definition:
Usage
Outcome
Fields
The fields field, allows you to create multi-dimensional content type fields (sub-fields). This is useful when you want to create a complex content type. In case you want to define a list data, you will have to use the block field.
When you specify the field type as fields, you need to define sub-fields within the fields property.
Properties
fields: Define the sub-fields of your content type. All the above types are supported.
Usage
Outcome
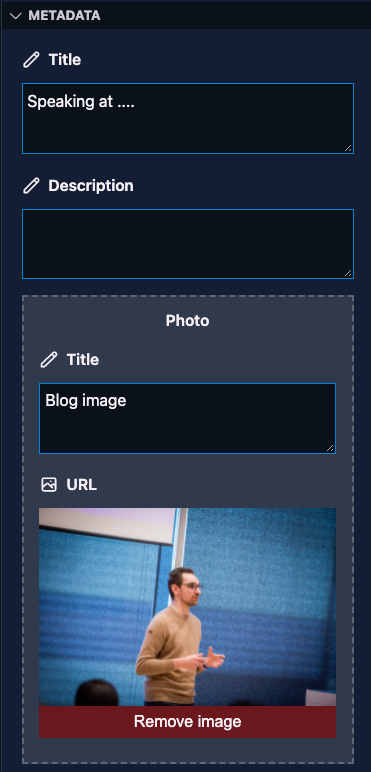
Block
The block field type allows you to define a group of fields which can be used to create a list of data.
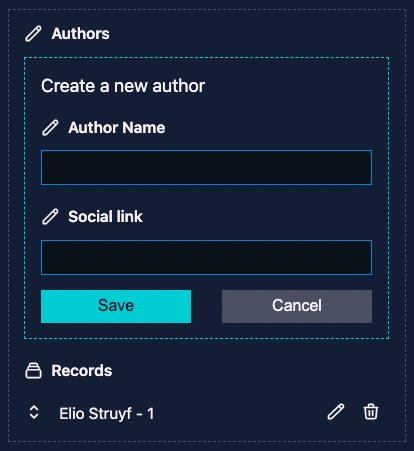
Prerequisites
To work with the block field type, you need to define a field group (a set of fields for your data) in the frontMatter.taxonomy.fieldGroups setting.
Info: You can use the same field types as you would use in the regular content types.
Properties
fieldGroup: Define the field group(s) that will be used to create a list of data.
Usage
Important: If you want, you can also create field groupings within the field grouping. This is useful when you want to create sub-groups of data.
Outcome
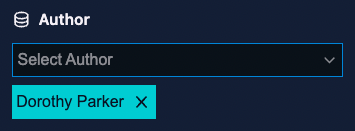
Data file
The dataFile field type allows you to use a data file to populate the field with a list of options. For instance, if you have a data file with all the authors of your site, you can use the dataFile field type to populate the authors field with the data from the authors data file.
Prerequisites
To use the dataFile field type, you need to have a definition for a data file in place. Here is an example of the authors sample:
Properties
dataFileId: Specify the ID of the data file to use for this field (required).dataFileKey: Specify the key of the data file to use for this field (required).dataFileValue: Specify the property name that will be used to show the value for the field (optional).multiple: Specify if you want to select one or multiple records (optional).
Usage
Outcome
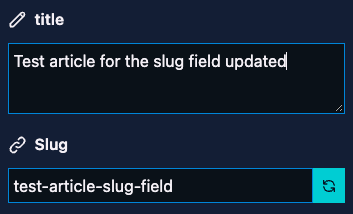
Slug
The slug field allows you to create/update the slug of the current page.
Properties
editable: Specify if you allow manual changes, or if the slug is generated automatically (optional - default:true).
Usage
The field is configured as follows:
Outcome
The above configuration gives you the following outcome:
Info: The slug is generated based on the title of the page. More information about it can be found in the generate slug command section.
Feedback
Do you want to provide feedback about this page/content?
Provide feedbackDid you spot an issue in our documentation, or want to contribute? Edit this page on Github!